Are you a member of the Splunk Community?
- Find Answers
- :
- Using Splunk
- :
- Splunk Search
- :
- How to Create "Impossible Travel" Security Monitor...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark Topic
- Subscribe to Topic
- Mute Topic
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
I have some reservations about the usefulness of this with so much more usage of IaaS/PaaS/SaaS these days...but since this is non-trivial to produce, I thought I would save everyone the work of developing from scratch if it is something you'd like to monitor. I would also like to note, this has bubbled up activity that was unauthorized/malicious in my experience...so maybe it's not useless...
This uses a macro built on the search string provided by @MuS in this post: https://answers.splunk.com/answers/90694/find-the-distance-between-two-or-more-geolocation-coordinat...
Prerequisites:
- normalized fields: user, src_ip
- geodistance macro
- well filtered base search of 10000 or less events OR
- streamstats
limits.confmax_stream_window = <adjusted for base search>DO NOT RAISE THIS ARBITRARILY in my environment I have raised this to an upper limit of +10% of my average base events (to include my max) over the past month after doing a LOT of filtering in the base search - filtering clauses to get this down to a manageable number of results
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- base search: as many indexes/data sources as might contain authentication, authorization, or access data that may be relevant for monitoring potential unauthorized or malicious activity
- filter out garbage IP addresses:
src_ip!=<rfc 1918 addresses> src_ip!=<whatever other garbage you don't need>maybe you don't really want to try to deal with IPv6 addresses, maybe you have a lookup that you can drop all your known public ip space - filter out garbage user data:
user!=*test* user!=<whatever other garbage you don't need> - normalize user: in my case I take whatever user attribute is in the base search, username or email address or whatever, and then query my IAM provider to return a standard value type for my user field, for example email address
- dedup for each user: from your base search you want each unique ip address and _time for each individual user, for me this took about 250K events down to about 30K, you would think including _time in the dedup would render the dedup useless but in this case it did not and _time is a critical field, you may also want to include index or sourcetype (whichever is applicable)
- prep for streamstats, the "current" data becomes the "destination": dest_time, dest_ip
- prep for streamstats, sort your data for each user and _time: streamstats needs to work a single user's data _time sorted so the results aren't broken into different sets (default limit of 10K)
- streamstats to create the "source" for each "destination": from the users previous event src_time, src_ip are generated (default limit of 10K)
- filter out garbage streamstats data: the first event for every user will have a null src_ip, and events with the same src and dest ip addresses are useless
- calculate geo statistics: the
geodistancemacro will take src_ip and dest_ip as arguments and return the city, region and country for each ip, the distance traveled in km and miles, hours it took to travel, and the kph and mph - additional filtering logic: in my case I dropped all events where mph are less than the speed of a commercial airplane as well as any events where the src and dest regions (such as a single U.S. state) are the same
- pretty print the output
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
| index=x OR index=y OR index=z src_ip!=192.168.* src_ip!=*:* user!=*test*
| lookup src_ips.csv src_ip as src_ip outputnew description
| where isnull(description)
| lookup users.csv attr1 as user outputnew email
| lookup users.csv attr2 as user outputnew email <etc iterate as necessary or however you do user normalization>
| eval src_user='email'
| dedup src_user src_ip index _time
| rex field=_time "(?<dest_time>^\d+)"
| rename src_ip as dest_ip
| sort 0 src_user dest_time
| streamstats values(dest_ip) as src_ip values(dest_time) as src_time by src_user window=1 current=false <the window and current options are KEY here>
| where isnotnull(src_ip) AND (NOT 'src_ip'=='dest_ip')
| `geodistance(src_ip,dest_ip)`
| where mph>575 AND 'src_region'!='dest_region'
| stats values(src_ip) as src_ip values(dest_ip) as dest_ip list(src_city) as src_city list(src_region) as src_region list(src_country) as src_country list(dest_city) as dest_city list(dest_region) as dest_region list(dest_country) as dest_country avg(miles) as miles avg(hours) as hours avg(mph) as mph by src_user
| eval miles=round(miles,2)
| eval km=round(km,2)
| eval hours=round(hours,2)
| eval mph=round(mph,2)
| eval kph=round(kph,2)
| eval src_ip=mvdedup(split((mvjoin((mvzip(src_ip,dest_ip)),",")),","))
| eval src_city=mvdedup(split((mvjoin((mvzip(src_city,dest_city)),",")),","))
| eval src_region=mvdedup(split((mvjoin((mvzip(src_region,dest_region)),",")),","))
| eval src_country=mvdedup(split((mvjoin((mvzip(src_country,dest_country)),",")),","))
| table src_user src_ip src_city src_region src_country miles km hours mph kph
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- base search: as many indexes/data sources as might contain authentication, authorization, or access data that may be relevant for monitoring potential unauthorized or malicious activity
- filter out garbage IP addresses:
src_ip!=<rfc 1918 addresses> src_ip!=<whatever other garbage you don't need>maybe you don't really want to try to deal with IPv6 addresses, maybe you have a lookup that you can drop all your known public ip space - filter out garbage user data:
user!=*test* user!=<whatever other garbage you don't need> - normalize user: in my case I take whatever user attribute is in the base search, username or email address or whatever, and then query my IAM provider to return a standard value type for my user field, for example email address
- dedup for each user: from your base search you want each unique ip address and _time for each individual user, for me this took about 250K events down to about 30K, you would think including _time in the dedup would render the dedup useless but in this case it did not and _time is a critical field, you may also want to include index or sourcetype (whichever is applicable)
- prep for streamstats, the "current" data becomes the "destination": dest_time, dest_ip
- prep for streamstats, sort your data for each user and _time: streamstats needs to work a single user's data _time sorted so the results aren't broken into different sets (default limit of 10K)
- streamstats to create the "source" for each "destination": from the users previous event src_time, src_ip are generated (default limit of 10K)
- filter out garbage streamstats data: the first event for every user will have a null src_ip, and events with the same src and dest ip addresses are useless
- calculate geo statistics: the
geodistancemacro will take src_ip and dest_ip as arguments and return the city, region and country for each ip, the distance traveled in km and miles, hours it took to travel, and the kph and mph - additional filtering logic: in my case I dropped all events where mph are less than the speed of a commercial airplane as well as any events where the src and dest regions (such as a single U.S. state) are the same
- pretty print the output
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
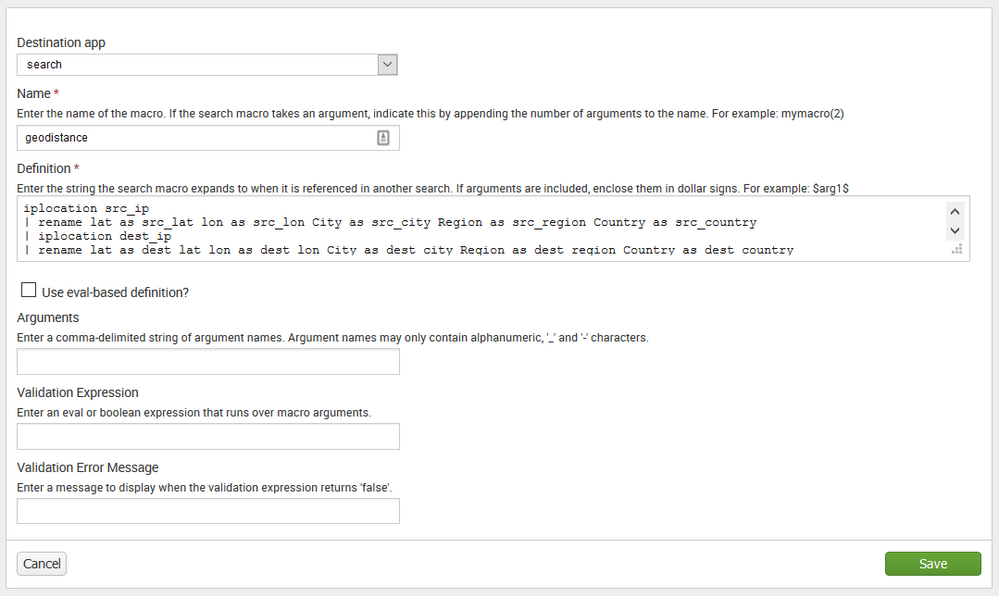
create a new macro with no arguments: "geodistance"
iplocation src_ip
| rename lat as src_lat lon as src_lon City as src_city Region as src_region Country as src_country
| iplocation dest_ip
| rename lat as dest_lat lon as dest_lon City as dest_city Region as dest_region Country as dest_country
| search src_lat!="," src_lon!="," dest_lat!="," dest_lon!=","
| eval lat=(dest_lat-src_lat)*pi()/180
| eval lon=(dest_lon-src_lon)*pi()/180
| eval dest_rad=dest_lat*pi()/180
| eval src_rad=src_lat*pi()/180
| eval a=pow(sin(lat/2),2)+pow(sin(lon/2),2)*cos(dest_rad)*cos(src_rad)
| eval miles=(12742*atan2(sqrt(a),sqrt(1-a)))*0.621371
| eval km=12742*atan2(sqrt(a),sqrt(1-a))
| eval hours=if(((dest_time-src_time)/60/60)=0,".01",(abs(((dest_time-src_time)/60/60))))
| eval mph=miles/hours
| eval kph=km/hours
| fillnull value=""
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
A thing of beauty marycordova - thank you!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
As an add-on here is my macro I use to get distances based on lat's and lon's 🙂
[distance(4)]
args = lat1,lon1,lat2,lon2
definition = eval rlat1 = pi()*$lat1$/180, rlat2=pi()*$lat2$/180, rlat = pi()*($lat2$-$lat1$)/180, rlon= pi()*($lon2$-$lon1$)/180\
| eval a = sin(rlat/2) * sin(rlat/2) + cos(rlat1) * cos(rlat2) * sin(rlon/2) * sin(rlon/2) \
| eval c = 2 * atan2(sqrt(a), sqrt(1-a)) \
| eval distance = 6371 * c | fields - a c r*
iseval = 0
It is part of my Dark Sky app featured in this .conf2017 talk https://conf.splunk.com/files/2017/slides/take-a-talk-into-the-art-of-dark-sky-photography-with-a-sp...
cheers, MuS
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Interesting.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
thanks! 🙂