- Find Answers
- :
- Splunk Administration
- :
- Monitoring Splunk
- :
- How to calculate max and actual search concurrency
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark Topic
- Subscribe to Topic
- Mute Topic
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Note: I'm answering my own question here for posterity as I'm sure others will want to find the answer. I haven't seen anyone provide good solution to this question.
Question: How does one calculate actual search concurrency usage and overlay with maximum search concurrency.
Answer to follow.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The Answer.
The calculation for max concurrent searches is
(max_searches_per_cpu * cpu_count + base_max_searches) * num_search_members
where ...
- max_searches_per_cpu - is a setting in limits.conf -> search stanza
- cpu_count - is actual real cores not virtual cores
- base_max_searches - is a setting in limits.conf -> search stanza
- num_search_members - is the number search heads in the cluster
The calculation for actual concurrent searches
Data is in the _audit index
The logic consists of
- find the start time of a search and increment the count +1
- find the end time of a search and decrement the count -1
- using streamstats one can achieve a running count
- the start time is found by using _time=exec_time
- the end time is found using _time=exec_time+total_run_time
- use makemv and mvexpand to generate the start and end times
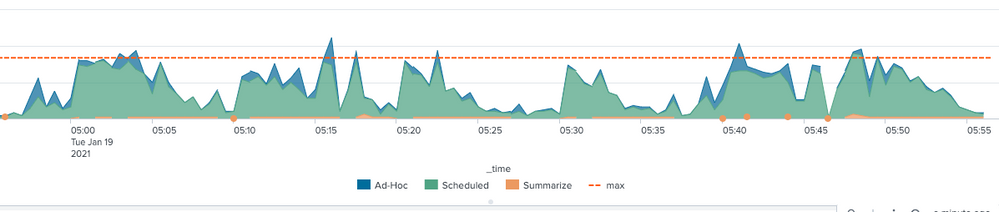
Example Timechart
- max concurrent searches is overlayed
- search type is stacked
Search
- Replace <search_heads> with your search head(s)
index=_audit action=search host=<search_heads> NOT "search_id='rsa_scheduler"
| fields - _raw
| eval search_type=case(match(search_id,"scheduler_"),"Scheduled",match(search_id,"SummaryDirector"),"Summarize")
| eval search_type=if(isnull(search_type),"Ad-Hoc",search_type)
| eval end_time=exec_time + total_run_time
| eval events=exec_time + " " + search_type + " 1:" + end_time + " " + search_type +" -1"
| fields _time events
| makemv delim=":" events
| mvexpand events
| rex field=events "(?<_time>\S+)\s+(?<type>\S+)\s+(?<incr>\S+)"
| fields - events
| sort 0 _time
| streamstats current=f sum(incr) as concur by type
| timechart span=30s first(concur) by type
| eval "max search concurrency" = [
| rest /services/properties/limits/search/max_searches_per_cpu
| fields splunk_server value
| rename value as max_searches_per_cpu
| append [
| rest /services/properties/limits/search/base_max_searches
| fields splunk_server value
| rename value as base_max_searches
]
| append [
| rest splunk_server=<search_heads> /services/server/status/resource-usage/hostwide
| eval cpu_count = if(isnull(cpu_count), "0", cpu_count)
| fields splunk_server cpu_count
]
| stats values(max_searches_per_cpu) as max_searches_per_cpu values(base_max_searches) as base_max_searches values(cpu_count) as cpu_count by splunk_server
| eval instance_max_concurrent_searches = (max_searches_per_cpu * cpu_count + base_max_searches)
| stats sum(instance_max_concurrent_searches) as max
| return $max
]
Please Upvote if you fine helpful
- Mark as New
- Bookmark Message
- Subscribe to Message
- Mute Message
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
The Answer.
The calculation for max concurrent searches is
(max_searches_per_cpu * cpu_count + base_max_searches) * num_search_members
where ...
- max_searches_per_cpu - is a setting in limits.conf -> search stanza
- cpu_count - is actual real cores not virtual cores
- base_max_searches - is a setting in limits.conf -> search stanza
- num_search_members - is the number search heads in the cluster
The calculation for actual concurrent searches
Data is in the _audit index
The logic consists of
- find the start time of a search and increment the count +1
- find the end time of a search and decrement the count -1
- using streamstats one can achieve a running count
- the start time is found by using _time=exec_time
- the end time is found using _time=exec_time+total_run_time
- use makemv and mvexpand to generate the start and end times
Example Timechart
- max concurrent searches is overlayed
- search type is stacked
Search
- Replace <search_heads> with your search head(s)
index=_audit action=search host=<search_heads> NOT "search_id='rsa_scheduler"
| fields - _raw
| eval search_type=case(match(search_id,"scheduler_"),"Scheduled",match(search_id,"SummaryDirector"),"Summarize")
| eval search_type=if(isnull(search_type),"Ad-Hoc",search_type)
| eval end_time=exec_time + total_run_time
| eval events=exec_time + " " + search_type + " 1:" + end_time + " " + search_type +" -1"
| fields _time events
| makemv delim=":" events
| mvexpand events
| rex field=events "(?<_time>\S+)\s+(?<type>\S+)\s+(?<incr>\S+)"
| fields - events
| sort 0 _time
| streamstats current=f sum(incr) as concur by type
| timechart span=30s first(concur) by type
| eval "max search concurrency" = [
| rest /services/properties/limits/search/max_searches_per_cpu
| fields splunk_server value
| rename value as max_searches_per_cpu
| append [
| rest /services/properties/limits/search/base_max_searches
| fields splunk_server value
| rename value as base_max_searches
]
| append [
| rest splunk_server=<search_heads> /services/server/status/resource-usage/hostwide
| eval cpu_count = if(isnull(cpu_count), "0", cpu_count)
| fields splunk_server cpu_count
]
| stats values(max_searches_per_cpu) as max_searches_per_cpu values(base_max_searches) as base_max_searches values(cpu_count) as cpu_count by splunk_server
| eval instance_max_concurrent_searches = (max_searches_per_cpu * cpu_count + base_max_searches)
| stats sum(instance_max_concurrent_searches) as max
| return $max
]
Please Upvote if you fine helpful